Evolution Briefing: Lonza announce new CEO
June 5, 2020
COVID Drug Strategies
June 9, 2020The Pfizer and BioNTech agreement expands the research and development alliance signed by the companies in 2018 to develop mRNA-based vaccines against influenza.
With the latest collaboration, the companies aim to speed-up the development of BioNTech’s BNT162 as a potential Covid-19 vaccine via the ‘Lightspeed program.’

BioNTech also formed a strategic development and commercialisation partnership with Shanghai Fosun Pharmaceutical to advance BNT162 for protection from Covid-19 in China. As part of the deal, the companies will co-develop the candidate in China and perform clinical trials by utilising Fosun’s clinical development, regulatory and commercial expertise in the country.

BioNTech’s Covid-19 vaccine
BioNTech’s Covid-19-focused project includes four vaccine candidates. Two of these candidates consist of a nucleoside modified mRNA, one includes a uridine containing mRNA and the fourth candidate has self-amplifying mRNA. The company has included a larger spike sequence in two of the vaccine candidates and the spike protein’s smaller optimised receptor binding domain (RBD) in the remaining two.
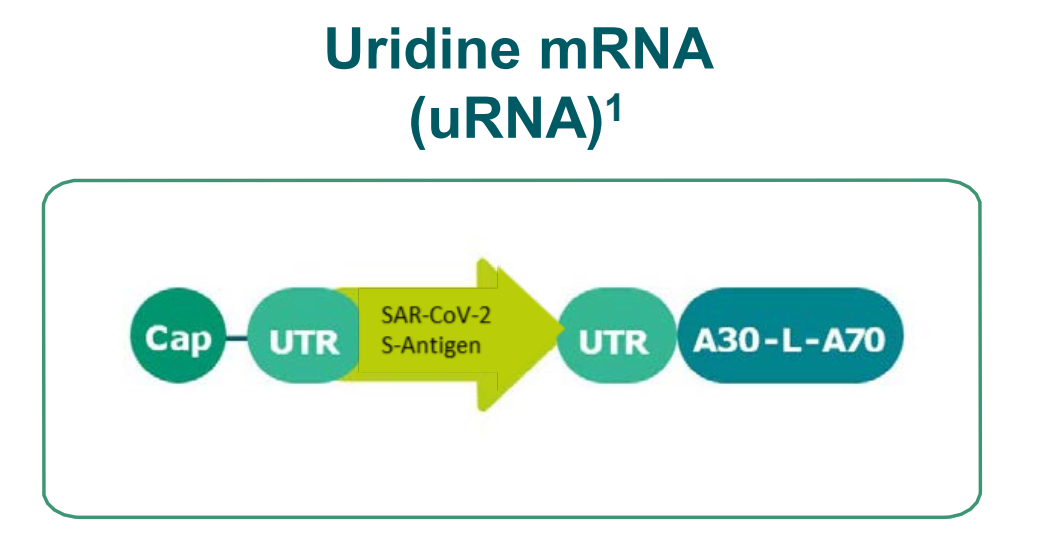
Rationale
- Prime / boost
- Strong adjuvant effect
- Active at low doses
- Strong antibody response
- CD8 T-Cells > CD4 T-Cells
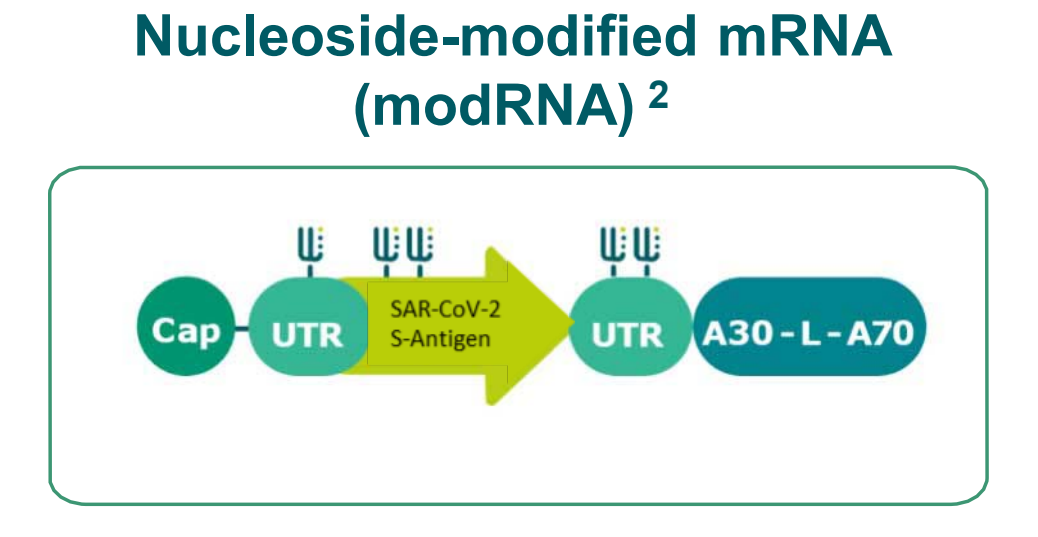
Rationale
- Prime/ boost
- Moderate adjuvant effect
- Very strong antibody response
- CD4 T-Cells > CD8 T-Cells
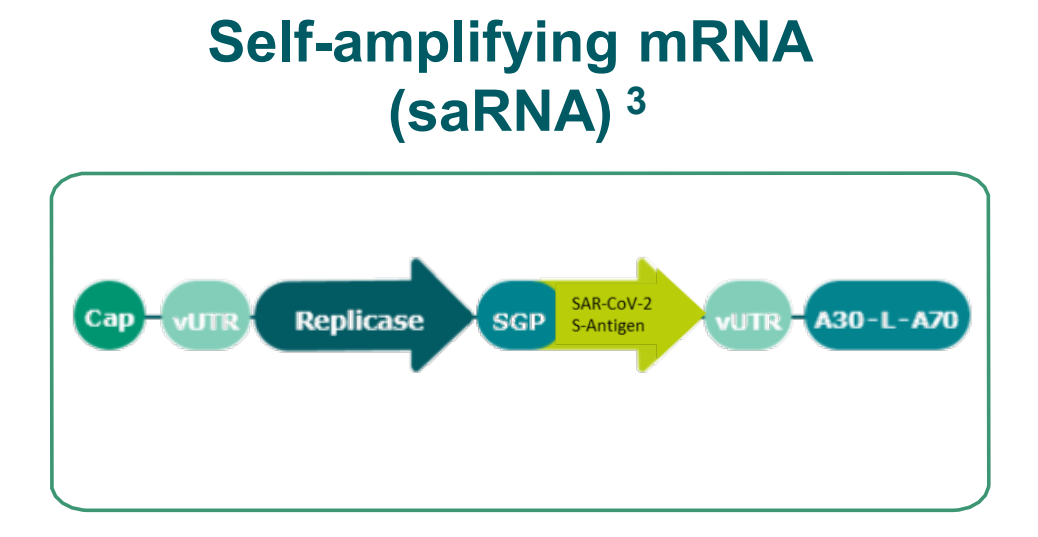
Rationale
- Prime (1x injection)
- Long-term activity
- Very strong antibody response
- Very strong T-Cell response (CD8 and CD4)
- Potent immune protection at low doses (approx. 60x lower dosages required to induce immunity vs. uRNA observed in preclinical models)